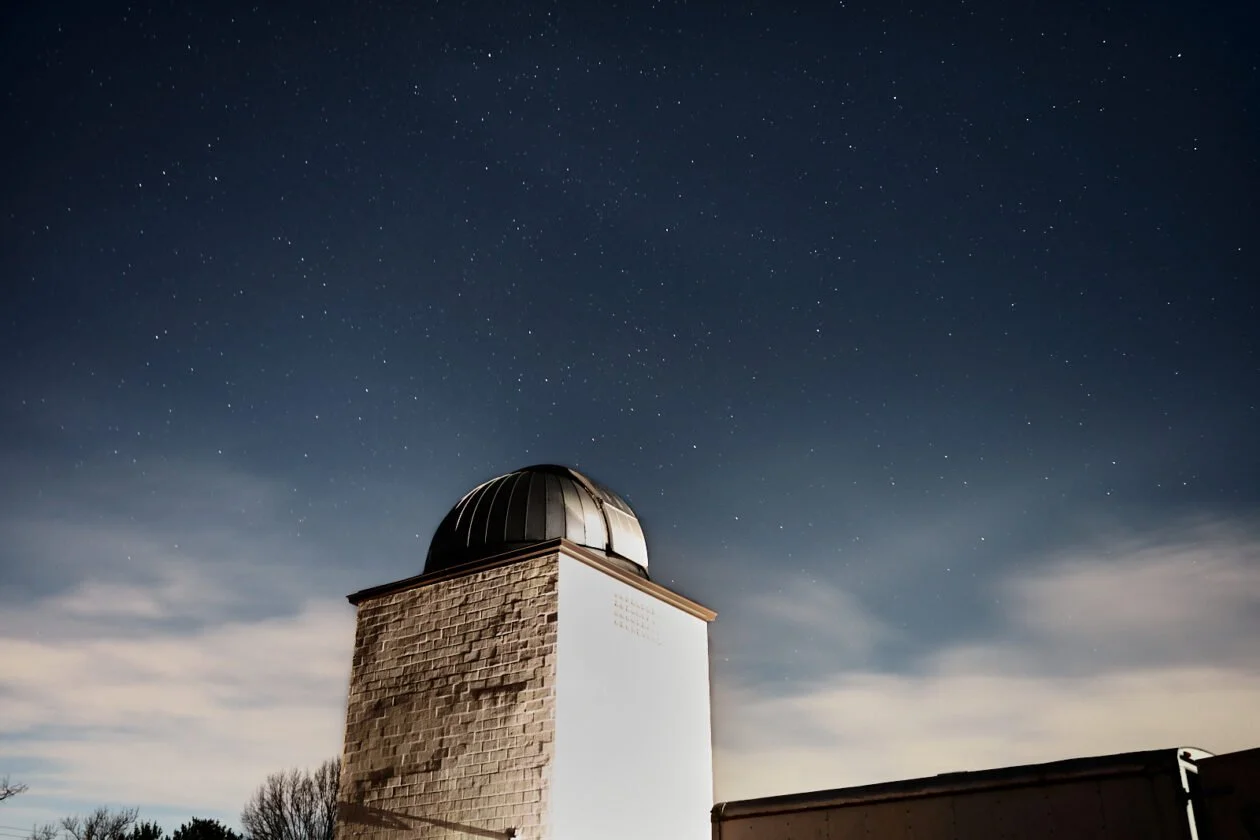
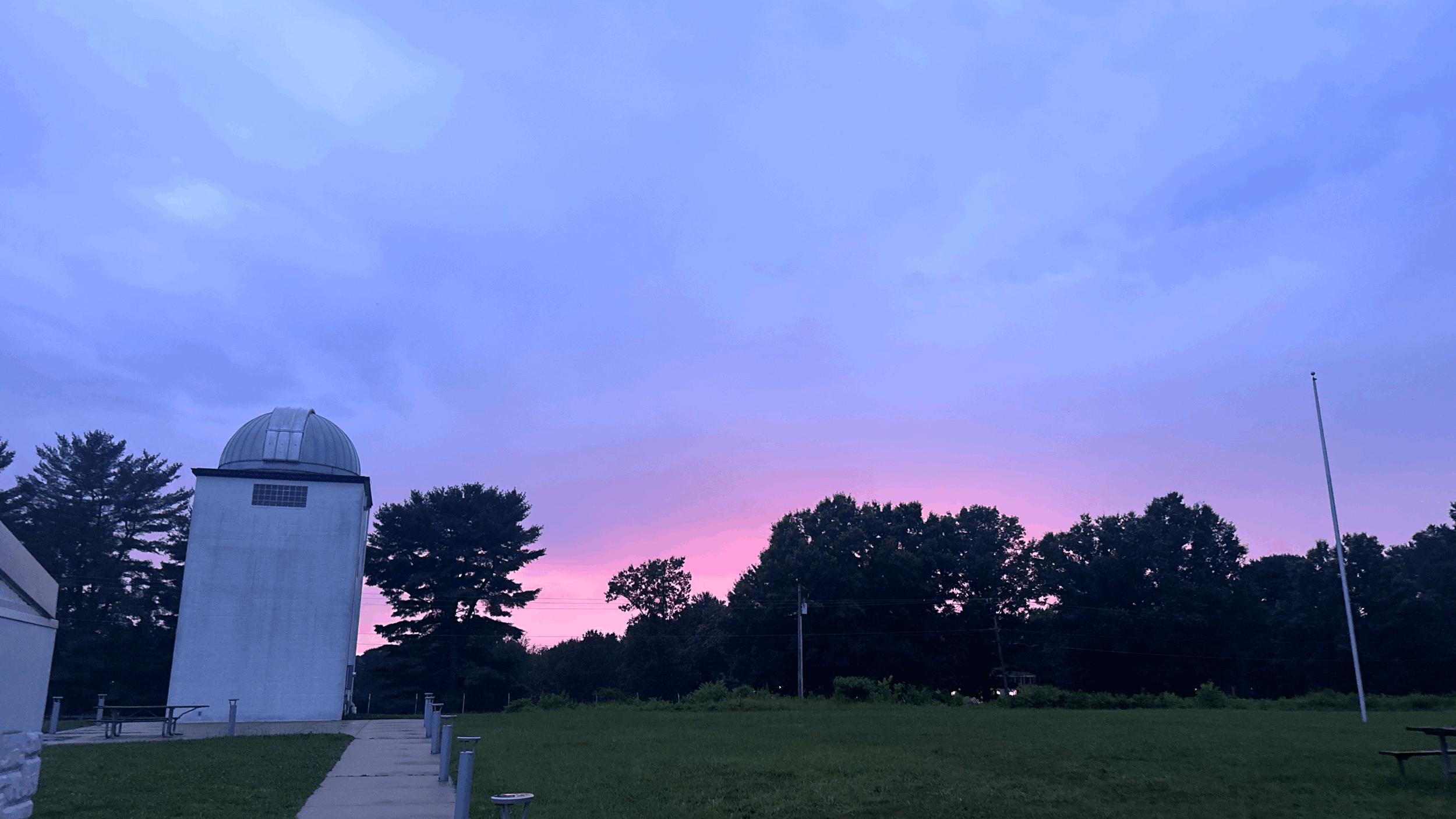
Turner Farm earns urban night sky designation for efforts to limit light pollution
The roll-top observatory at Turner Farm Park (courtesy Fairfax County Park Authority)
originally published in ffxnow 22 January 2026
written by Emily Leayman
https://www.ffxnow.com/2026/01/22/turner-farm-earns-urban-night-sky-designation-for-efforts-to-limit-light-pollution/
Light pollution continues to be a concern in the populous Northern Virginia region, but one Fairfax County park has taken steps to protect the night sky.
DarkSky International has designated Turner Farm (925 Springvale Road) in Great Falls as an International Dark Sky Urban Night Sky Place, a certification reflecting its efforts to protect the night sky from light pollution. The Fairfax County Park Authority noted that Turner Farm is one of a few places to view a relatively dark sky near D.C.
Eileen Kragie, the founder of Dark Sky Friends and chapter leader of DarkSky NOVA, told FFXnow the accolade has been in the works for four years and is a “huge achievement for Fairfax County and for Northern Virginia.”
“The strong community support and partnerships were essential for bringing this to fruition,” Kragie said. “Being in the shadow of the Nation’s Capital means the education programs and night viewing will reach this entire DMV and hopefully help turn back the tide of the growth of light pollution in this region.”
To earn the designation, the park authority and its partners implemented a lighting management plan with low-level and warm-spectrum lighting, replaced park lighting with DarkSky-compliant lighting fixtures and 2,700K bulbs, and expanded its astronomy and light pollution educational and outreach programs.
Fairfax County leaders also voted in late 2023 to adopt a special ordinance limiting outdoor lighting for a half mile around the park’s observatory.
“This designation reflects the Fairfax County Park Authority’s commitment to protecting natural resources that directly support the health and well-being of our community,” said Jai Cole, executive director of the Fairfax County Park Authority. “By reducing light pollution, we are supporting wildlife, conserving energy and creating spaces where people can slow down, look up and feel connected to something bigger.”
The park authority will host a Dark Sky education and celebration event to mark the accolade at 6 p.m. tomorrow (Friday). The event at Turner Farm’s observatory will include remarks from project partners, educational activities and night sky viewing.
The cap on attendance has been reached, according to the park authority. In the case of inclement weather, which is appearing increasingly likely, the event will be relocated to the Colvin Run Mill Education Center (10017 Colvin Run Road).
An FCPA spokesperson says the agency doesn’t plan to postpone the event, since the coming winter storm isn’t expected to arrive until Saturday evening. However, an update will be shared if that changes.
Turner Farm, which was once a dairy farm, has an observatory that was first developed under the U.S. Army Map Service. Today, the observatory is open during public viewing nights, programs and permitted events through a park authority partnership with the Analemma Society.
Appreciating and preserving the wonder of a star-filled sky
Big Dipper over Sky Meadows State Park
a DarkSky International designated Dark Sky Park
photo credit: Kandi Mitchell
Originally published by College of Science George Mason University
Apr 17, 2025
Written by Tracy Mason
The wonder inspired by gazing at a star-filled sky has deep philosophical and cultural significance, reinforcing the importance of studying the heritage of the night sky.
Next week, April 21 to 28, 2025, is International Dark Sky Week, a global celebration of the night. Here are some of our college‘s multidisciplinary efforts to contribute to the science and support of the issue of light pollution along with ways you personally can appreciate our shared night sky.
Did you know George Mason has an Observatory on the Fairfax, VA campus? The largest on-campus observatory in the mid-Atlantic region and the second largest on the east coast, the George Mason University Observatory mission is to inspire curiosity, foster scientific understanding, and ignite a passion for the wonders of the Universe among people of all ages and backgrounds. By embracing innovation, scientific rigor, and a passion for discovery, the George Mason University Observatory aspires to be a catalyst for scientific learning, and a cherished community resource, fostering a shared sense of awe and appreciation for the marvels of the night sky and beyond.
One of their foundational pillars is the conservation of Dark Skies, recognizing the importance of preserving our natural environment and reducing light pollution. The Observatory team advocates for the conservation of dark skies through educational initiaitives, aiming to raise awareness about the impact of light pollution on astronomy and the environment.
Did you also know that Department of Environmental Science and Policy chair Gad Perry’s chapter on Night Lights and Reptiles is included in the go to resource on Artifical Light at Night (ALAN): Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting. Published in 2006, it is still considered by many as the leading book on light pollition and ecology. Several dark sky advocates mention it was this body of work that got them into fighting light pollution. In his recent video series posted on social media, Perry explains how urban ecology can pave the way for the encompassing goal of One Health to succeed. Urban green spaces can support a thriving co-existence between people and many different species, a win-win situation.
How can our science community, and all across George Mason including the larger surrounding community, better understand about light pollution and support this effort?
George Mason University alumna, founder of Dark Sky Friends and the DarkSky NOVA Chapter Leader, Eileen Kragie is working hard to build awareness and advocacy for the issue of light pollution in our region and across the state. According to Kragie, Virginia leads the east in dark sky conservation with five designated International Dark Sky Parks (the largest number of International Dark Sky Parks of any state east of the Mississippi), demonstrating a strong commitment to preserving the night sky. The work being done at the George Mason University Observatory and the College of Science plays a significant role in education and policy advocacy for dark sky conservation at both the state and regional levels. The College of Science actively supports local efforts in dark sky conservation and education, participating in DarkSky International’s local chapter, DarkSky NOVA, with Observatory directors and an astrophysics students serving as chapter leaders.
Higher education and research are crucial to study the full range of light pollution’s impacts, including effects on wildlife such as birds, fireflies, hatching turtles, nocturnal creatures, and plants, as well as its influence on human physical and mental health.
According to its Director Rob Parks, the George Mason Observatory is moving forward on an undergraduate research project this summer to create a light map of the George Mason University Fairfax Campus. “This may aid in future policy and decision making with an intent of basing sensible policies on a data driven approach,” Parks explained.
Curious about what you can do? How about taking the Dark Sky pledge and assessing your home or business dark sky friendliness by following the Five Principles of Responsible Outdoor Lighting at Night.
As Kragie said... “All of the education and awareness is great, but if it is not effecting behavioral change then what is it all for?”
Mayor Colbert Town of Vienna, Virginia proclaims 21-28 April 2025 International Dark Sky Week
Town of Vienna Mayor Linda Colbert and Dark Sky Friends founder & DarkSky NOVA chapter leader Eileen Kragie with International Dark Sky Week 2025 Proclamation
Photo credit Town of Vienna
Thank you Mayor Colbert and Town of Vienna, VA - Government council for recognizing and celebrating DarkSky International's International Dark Sky Week with us all!
Dark Sky Friends founder and president and DarkSky NOVA chapter leader Eileen Kragie accepts Town of Vienna, VA - Government's International Dark Sky Week Proclamation from Mayor Colbert.
Light pollution can take a toll on wildlife, our health and the environment. To help raise awareness about its harmful effects, Mayor Linda Colbert proclaimed April 21-28, 2025, as International Dark Sky Week in the Town of Vienna at tonight's regular Town Council meeting. To learn how you can reduce light pollution, visit www.darksky.org.
Watch the presentation of the Town of Vienna’s proclamation here.
Falls Church City Council Issues April 14 Proclamation Declaring City-Wide "Dark-Sky Week," April 21-28
Falls Church City Virginia International Dark Sky Week 2025 Proclamation
photo credit eileen Kragie
Originally published in The Falls Church Independent 16 April 2025
F.C. City Council Issues April 14 Proclamation Declaring City-Wide "Dark-Sky Week," April 21-28
Once again, the City of Falls Church is helping shed light on the problem of global and regional light pollution and its negative effects on living beings around the world.
Light pollution is the "human-made alteration of outdoor light levels from those occurring naturally," according to DarkSky International. And its disruptive effects harm: "wildlife and human health, wastes money and energy, contributes to climate change, and blocks our view of the universe."
On April 14, the City issued a Proclamation – signed by Mayor Letty Hardi and passed by the City Council – in support of "Dark-Sky Week," for the City, April 21-28.
The purpose of the week, per the Proclamation, is to "urge all to celebrate the pristine and undisturbed dark skies throughout the Commonwealth, and take a moment to ponder their role in protecting this valuable resource and connection to the environment now and for future generations."
The week is designed to "raise awareness of light pollution, and provide free education, resources, and solutions to the public to encourage the protection of and enjoyment of dark skies and responsible outdoor lighting."
"Thank you Mayor Hardi and City of Falls Church Government City Council members for recognizing 21-28 April 2025 as Dark Sky Week in Falls Church!!," posted DarkSky NOVA – the Virginia chapter of DarkSky International – on Facebook yesterday April 15. "Falls Church City joins in the global celebration for IDSW [International Dark Sky Week], raising awareness of light pollution and educating its residents."
Eileen Kragie, chapter leader of DarkSky NOVA receives City's proclamation declaring Dark Sky Week in Falls Church from April 21-28. Photo courtesy Eileen Kragie via Facebook.
Per the City's proclamation, "the aesthetic beauty and wonder of a natural night sky is a shared heritage of all humankind, and the experience of standing beneath a starry night sky inspires feelings of wonder and awe and encourages an interest in science and nature, especially among young people and out-of-area visitors to Virginia's local communities."
With the "greatest number of Dark-Sky Parks east of the Mississippi" located in Virginia, "home to dozens of species who rely on undisturbed night environments to hunt mate and thrive," and with "80 percent of the world's population, including many people in Virginia [living] under a dome of light pollution ... [who] may never experience the visual wonder or ecological and health benefits of living under a dark sky," increased community awareness of light pollution is essential, the Proclamation declared.
Dark-Sky Week Proclamation passed by the City Council April 14, 2025. Facebook photo courtesy DarkSky NOVA.
Following the City Council's Dark-Sky Week Proclamation ceremony, DarkSky NOVA chapter head, Eileen Kragie, wrote to The Falls Church Independent to update us on her organization's recent efforts to combat light pollution and some of the challenges faced.
"There are some terrible lights in FC," Kragie said. "Just in front of the Cherry Hill Park are examples of the acorn lights which are awful for light pollution and glare.... The lights on the school further down are [also] blinding and dangerous."
Acorn light, "awful for light pollution and glare," in downtown Falls Church City. Photo courtesy Eileen Kragie.
"What is really needed is a committed group of residents who will work on this issue regularly and hold events. Encouraging everyone, homeowners and businesses to assess their home and business lighting and to adopt the 5 principles of responsible outdoor lighting at night will go a long way in addressing the problem."
"There are just so many jurisdiction in this area which desperately need work," Kragie continued. "And everyone must begin to voluntarily adopt responsible lighting practices. We don’t throw our litter on the ground anymore. We need to stop littering with our lights."
For more information in International Dark Sky Week 2025, go here.
For a recent letter-to-the-editor on combatting light pollution from DarkSky NOVA's chapter leader, Eileen Kragie, see our article below:
F.C. Bulletin: City Manager Proposes FY′26 City Budget; Letter-to-the-Editor; F.C. Arts
The Falls Church IndependentChristopher Jones
City of Falls Church International Dark Sky Week Proclamation 2025 21-28 April
Dark Sky Friends Founder and President Eileen Kragie accepting City of Falls Church Virginia International Dark Sky Week 2025 Proclamation
Presentation of 2025 International Dark Sky Week Proclamation by City of Falls Church Virginia to Eileen Kragie, Founder and President of Dark Sky Friends by Mayor Hardi and city council members 14 April 2025.
Minute 14:43- 18.57 or click on item agenda e
Reduce Light Pollution to Protect Bird Migration
Today's letter-to-the-editor by Eileen Kragie addresses the crisis to migrating birds in our region from light pollution and asks Falls Church City residents and the City to join in efforts to protect the millions of birds at risk. Photo courtesy Fairfax County. ~ The Falls Church Independent. 25 March 2025
Originally letter-to-the-editor published March 25, 2025 in The Falls Church Indpendent
Dear Editor,
Spring is upon us. A new Lights Out for the Birds initiative for the Spring bird migration season was launched by the Northern Virginia Bird Alliance in partnership with a number of other organizations including DarkSky NOVA, the Northern Virginia chapter of DarkSky International.
We need the support of every resident, business and government entity in the region to protect the hundreds of millions of birds traversing our region now.
One hundred million birds migrate over our heads at night in the Spring as we sleep, resting during the day and singing more to attract mates. After summering in their Northern homes, 160 million return on the Fall migration with their new families.
Migrating birds can be severely affected by light pollution. Courtesy Fairfax County.
Hundreds of millions of birds die each year due to collisions with buildings and homes or simply of exhaustion from being attracted to artificial lights at night. Birds use the stars and moon to navigate by. Too many lights confuses them and draws them off course. Too often the result is fatal.
See this video, "Lights Out Texas – Dimming Lights for Birds - Documentary" to learn more.
The City of Falls Church’s neighbor, Fairfax County has undertaken measures to protect the migrating birds this season. The Fairfax County Board of Supervisors has been, and is, very supportive of the light pollution issue especially the deadly harm it causes the birds migrating through our Northern Virginia area.
Fairfax County Board Supervisor Walkinshaw introduced a joint board matter with Supervisor Jimenez, Supervisor Stark, and Supervisor Alcorn to address the problem and to raise awareness among the citizens and businesses of the county.
These measures include providing more information to residents about the importance of lighting responsibly especially during this time of year and instructing county staff to evaluate county owned buildings to turn off unnecessary lights. Educational information at the county level is being distributed about the problem, what citizens can do to help, and each individual supervisor is including information in their district newsletters.
The Fairfax County Park Authority is doing the same and several years ago created a webpage about Dark Skies and light pollution.
While time ran a little short to reach out to more local jurisdictions, we are asking everyone in the City of Falls Church to participate in this program and to help share it with family, friends and colleagues. It would be great if your paper could help promote this campaign.
I know the City of Falls Church is doing some wonderful work addressing this problem of light pollution. The City of Falls Church issued proclamations for International Dark Sky Week the past several years, demonstrating their support for this issue in addition to the outdoor lighting ordinances the city has enacted.
International Dark Sky Week falls 21 through 28 April this year at the height of the Spring bird migration season which is a great way to learn more about the wide range of impacts artificial light has at night, including our own human health.
DarkSky International has a program to certify your home "dark sky friendly," which is neighbor and community friendly, and can be applied to businesses too. We encourage everyone to take the time to assess your own home’s or business’s lighting, and to take the steps to make it dark sky friendly.
Remember dark skies do not mean dark ground. Lighting responsibly enables humans to traverse their spaces safely without harming our shared environments around us. Light pollution is doubling every 8-10 years and in some places scientists predict no stars will be visible in 20 years unless we take action now.
The lack of awareness among the public about this issue is a serious problem across the region, the country and the globe.
Many organizations are working together to educate about this easily solved pollution. Simply following the 5 Principles of Responsible Outdoor Lighting at Night will solve it. Is your lighting 1. Useful, 2. Targeted, 3. Low Level, 4. Controlled, and 5. Warm-Colored?
Please join us in being part of the solution to save the birds and to solve light pollution. And we invite you to join DarkSky NOVA. With all of us working together we can bring back the stars at night, protect our feathered friends as they travel through – the wildlife, nocturnal pollinators and plants too.
Thank you Falls Church Independent for all of the help you're giving to educate people around here!
~ Eileen Kragie, Vienna, Virginia.
Eileen Kragie is the founder of Dark Sky Friends, a DarkSky NOVA Chapter Leader, and a DarkSky International Advocate.
Fairfax County Lights Out for the Spring Bird Migration
photo credit Yiran Ding @yiranding
Link to Fairfax County Board of Supervisors Meeting 4 March 2025
Go to 4 March 2025 meeting. Board Matter begins at 2:01:42
Supervisor Walkinshaw:
Thank you, Mr. Chairman. I would like to begin by addressing several board matters. The first is a joint board matter with Supervisor Jimenez, Supervisor Stark, and Supervisor Alcorn.
Billions of birds migrate each year, traveling hundreds of miles between their wintering and breeding grounds. Along the way, they face numerous threats. Scientists have found that most of these birds migrate at night, using the stars to navigate. In Northern Virginia, between 100 and 160 million birds migrate each spring and fall. Unfortunately, the bright lights on tall buildings and sky glow attract them, leading to window collisions and exhaustion from circling illuminated structures. At dawn, these birds face additional urban threats.
North America's migratory bird population has declined by 2.9 billion birds over the past 50 years, a 30% drop. Fairfax County lies along the East Coast flyway, which serves as a superhighway for migrating birds. This makes our actions at the local level critical.
Several organizations, including Nature Forward, the Northern Virginia Bird Alliance, and Friends of Huntley Meadows, have partnered with Dark Sky Nova to launch the "Turn Lights Out for Birds" campaign. This campaign, running from March 15th to May 31st, urges residents and businesses to reduce unnecessary nighttime lighting.
Research on a Chicago high-rise found that this simple step reduced bird deaths by 80% while also cutting energy use and costs.
Mr. Chairman, I move that the Board of Supervisors support the Northern Virginia Bird Alliances' "Turn Lights Out for Birds" Spring campaign by directing the Office of Public Affairs to promote it before migration season begins on March 15th. Additionally, I move that the county executive identify county facilities where nighttime lighting could be reduced or eliminated during spring migration.
Chairman McKay: I'm happy to second the motion.
Mason Space Day 2024
Mason Space Day 2024 included light pollution as a topic in this year's line up of speakers.
This year light pollution was added as a topic for the presentations at George Mason’s Space Day. Home to the second largest on-campus observatory on the East coast, light pollution affects the professional astronomers studying and conducting research at George Mason University.
Full presentation of speakers at this year’s Mason Space Day.
Eileen Kragie of Dark Sky Friends and Tom Reinert of DarkSky International talk about the impacts of light pollution and how campuses, as small cities, contribute to the scale of light pollution in their communities. And the solutions.
Eileen and Tom’s presentation begin at 1:59:07. Dr Peter Plavchan’s immediately follows. He describes the how bright a 100 watt light is in comparison to the light of a full moon.
Take your Health Seriously by Embracing the Dark
The human circadian rhythm has been thrown into disarray because of an ever increasing amount of light pollution. Exposure to excess artificial lighting at night severely disrupts our natural cycle.
Photo credit Chaney Zimmerman
article written by ~ Nicole Caplan, Environmental Science Duke University
Take your Health Seriously by Embracing the Dark By: Nicole Caplan
As humans, each of us carries an internal clock that regulates our body’s perception of time. The steady melody of this clock’s chimes signifies when physiological processes are to occur, among which include sleep patterns, hormone production, digestion, and temperature regulation. These physical, mental, and behavioral changes that transpire over a 24-hour period are referred to as one’s circadian rhythm. Basic physiological processes that keep us alive rely on the synchronized rhythm of each person’s unique biological clock to function. Thus, a balanced circadian rhythm is essential for health and well-being.
The human circadian rhythm has been thrown into disarray because of an ever increasing amount of light pollution. Exposure to excess artificial lighting at night severely disrupts our natural cycle. A structure in the hypothalamus called the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) is like the grandfather clock of the brain. The SCN decides when the pineal gland should secrete melatonin, a hormone that aids sleep. Normally, light exposure during the day prevents melatonin secretion so that we can stay awake, while darkness at night does the opposite so we can doze off and recharge.
However, overabundant lighting, specifically blue light, confuses the SCN’s directions. When our eyes make contact with blue light, photoreceptors in the retina send signals to the SCN that light is flooding the senses, which causes the suppression of melatonin. This becomes quite a problem, considering we need melatonin to sleep. Interference in this hormone’s production leads to a plethora of health problems.
Most intuitively, melatonin suppression leads to the onset of sleep disorders like insomnia. Other mental health concerns also come with a lack of sleep. Early research has shown that melatonin has anxiety-reducing effects. Reduced melatonin can thus interfere with sleep and worsen symptoms of depression and anxiety. On top of that, disruptions to the sleep-wake cycle increase the potential for obesity, early onset-diabetes, and certain cancers. Studies indicate that melatonin assists in activating lymphocytes, cells in the immune system that fight off cancer. This means that decreased melatonin levels increase cancer risk. One individual hormone can control so much.
The need to maintain a regulated circadian rhythm that allows for an adequate production of melatonin at night is clear. Unfortunately, light pollution makes this balance difficult to sustain. So, with a never ending expansion of artificial lighting, how can we protect our health? The most important goal is to be mindful of what light to use and at what times.
Warm-colored bulbs with a correlated color temperature (CCT) of 2200 K or lower are ideal for nighttime, while cool-colored lights are ideal during the day. Also, shielded fixtures that minimize glare are recommended for outdoor lighting and use of screens and indoor LED lighting should be restricted at night. Furthermore, we should abide by the Five Principles for Responsible Outdoor Lighting and use light only as needed.
All these guidelines can help ensure that the internal chronometers that reside in our brains tick with a thoughtful cadence; alert during the day and restful at night.
DarkSky NOVA, Northern Virginia's New DarkSky International Chapter
Dedicated to preserving the beauty of the nighttime environment and safeguarding communities from the negative impacts of light pollution
Photo credit Bettymaya Foott. Light pollution under a night sky
Written by Eileen Kragie originally published in The Patch 3 July 2024
Light pollution is growing at twice the rate of the population, doubling every 8 years and in some places scientists predict NO stars will be visible in 20 years. We live in one of those places in Northern Virginia and the Washington D.C. metropolitan area.
A new Northern Virginia chapter of DarkSky International, DarkSky NOVA, has been created to educate Northern Virginians about the effects and impact of light pollution in their lives and to work with local and regional governments, businesses, organizations and residents to stop and to reverse light pollution and light trespass.
While Virginia has the largest number of DarkSky International designated parks of any state east of the Mississippi, the Observatory at George Mason University is the largest on-campus observatory in the mid-Atlantic region and coming soon, Observatory Park at Turner Farm in Great Falls will join DarkSky International’s prestigious list of dark sky sites, we live with light pollution levels on par with Los Angeles and other large metropolitan cities.
Light pollution is the result of bad lighting: unshielded, misaimed, too many, too bright, too white and on all night.
Bad lighting is the result of human behavior and that behavior can be changed.
Its sources include building exterior and interior lighting, advertising, commercial properties, offices, factories, streetlights, and illuminated sporting venues.
Residential lighting is an increasing and rapidly growing problem particularly when it comes to neighbors’ lighting.
What are the effects of light pollution?
A growing body of evidence links the brightening night sky directly to measurable negative impacts on:
Even the smallest amount of light negatively affects our health and that of the nocturnal pollinators, fireflies, nocturnal creatures, and plants. Light pollution has been linked to cancers, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disorders, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, and more.
Light pollution affects everyone, human and non-human alike. Fortunately, concern about light pollution is rising dramatically. A growing number of scientists, homeowners, environmental groups, and civic leaders are taking action to restore the natural night.
The good news is that light pollution, unlike many other forms of pollution, is reversible, and each one of us can make a difference. Just being aware that light pollution is a problem is not enough — we need to take action.
We can warm it, and dim it, and aim it down. Keep light out of the sky and put it on the ground. We can keep it out of our neighbor's windows and out of our parks.
We learned to be water wise. We can learn to light wisely. Let's stop wasting light. Light is energy, energy costs money. How much of your budget and tax dollars are being spent on wasted light?
To protect the night and stop light pollution and light trespass follow the Five Principles for Responsible Outdoor Light at Night, jointly published by DarkSky International and the Illuminating Engineering Society.
Light where you need it, when you need it, in the amount needed, and no more. If light is deemed useful and necessary, follow these guidelines to prevent, or when that’s not possible, minimize light pollution.
Certify your home Dark Sky Friendly and encourage your neighbors and community (schools, businesses, governments, local and religious organizations) to do the same
Do you know if your home lighting is community and night sky friendly?
DarkSky International’s Home Lighting Assessment helps you identify problem lighting and solutions that can reduce light pollution. Most people will find that a few simple changes can lead to lighting that is both beautiful and functional, without contributing to excessive light pollution.
It is time to start thinking about your use of outdoor light at night and to use it responsibly, kindly and considerately.
Join DarkSky NOVA and do your part to protect, to preserve and to reclaim the night skies over Northern Virginia.
International Dark Sky Week brings light pollution awareness
International Dark Sky Week Proclamation issued by Fairfax County Virginia Board of Supervisors
Article originally published in Fairfax Times 5 April 2024
The Fairfax County Board of Supervisors unanimously agreed to designate the week of April 2-8, 2024 as International Dark Sky Week. Chairman Jeff McKay and the board members issued a proclamation to celebrate the week and to bring awareness for the problems light pollution causes.
International Dark Sky Week is a worldwide night celebration to build awareness about the harmful effects of light pollution and the importance of the global nighttime environment. To learn more visit https://bit.ly/3J1nqB3
Light pollution is growing at twice the rate of the population, doubling every eight to 10 years, and in some places scientists predict in 20 years NO stars will be visible. Fairfax County is one of those places.
Along with blotting out the view of the night sky, light pollution negatively affects many parts of our world, including migratory birds, nocturnal pollinators, sea turtles, fireflies and other nocturnal creatures.
Light pollution also has serious human health consequences and has been linked to cancers: breast and prostate, anxiety, depression, high blood pressure, heart disorders, obesity, diabetes and, of course sleep disorders.
It is time light pollution is raised to the same level of priority as air and water pollution. It is that dangerous and that deadly.
Local, state, regional and national cooperation is needed to solve this pollution. Fortunately Fairfax County has made light pollution one of the county’s environmental goals for years.
Strong legislation and updated outdoor lighting codes and ordinances are critical to halting and to reversing this problem.
Robust public education campaigns and messaging are needed to raise awareness for everyone about the responsible use of outdoor light at night. The Fairfax County Park Authority Dark Skies page at https://bit.ly/3vysQR0 helps do just that.
For International Dark Sky Week this year, Fairfax County Public Library branches now have a Dark Skies backpack available for check out. The backpacks contain a light pollution monitoring kit to help measure the growth of light pollution in Fairfax County and star charts. Find more information at https://bit.ly/43F9PZw
A simple step that anyone can do is to take the Home Lighting Inventory developed by DarkSky International and certify your home Dark Sky Friendly. You can find the survey at https://bit.ly/3J2zkuu
Businesses and municipalities can do the same.
The steps are easy. Check to make sure that your lights are useful, are fully shielded, that the light does not trespass (targeted), that they are no brighter than necessary which saves money and prevents glare, that they use the warmest color temperature needed for the use. Use amber toned lighting or the color of candlelight. Use dimmers and timers.
And of course, simply turn off lights when they’re not needed. All of these steps prevent light trespass.
I don’t have a right to trespass on to your property. Why do my lights?
This year for International Dark Sky Week educate yourself on how to use outdoor light at night responsibly and ask yourself, will we be the last generations to see stars overhead in Fairfax County?
You will still be able to see solar eclipses however. This year’s International Dark Sky Week was chosen to coincide with the upcoming one. Both George Mason Observatory in Fairfax and Observatory Park at Turner Farm in Great Falls are holding partial eclipse viewing events on April 8.
After the total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, the next total solar eclipse that can be seen from the contiguous United States will be on Aug 23, 2044. Celebrate International Dark Sky Week and this once in a 20 year opportunity at these renowned Fairfax County observatories.
More information can be found at the following links: https://bit.ly/3VKJqrp and https://bit.ly/4a7Aalz
Eileen Kragie is the founder of Dark Sky Friends, an organization that advocates for responsible outdoor lighting at night.
Holiday Lights, No Stars
Photo credit e kragie
First published in The Fairfax Times 29 December 2023
Too sad for words. Instead of stepping outside on a cold winter night, to look up into a sky filled with a billion stars and planets twinkling overhead, we step out into a world awash with artificial light.
Light littering, trespassing, polluting and killing. The pristine night sky visible for eons, blotted out by excessive manmade light.
A sacred time of the year further polluted by massive strings and displays of artificial lights. Stripped of its mystery.
Where 20 or 30 years ago, this was a magical time of year to walk down the street, to see trees lit inside homes and subtle, minimal displays of holiday lights outside, it has now turned into a time where huge over lit displays are erected. More lights added each year, eroding the magic and sacredness of this time of year.
Communities encourage this by holding contests. Retailers encourage this by selling more and more lights. Businesses popping up who will install the lights on homes for you. The result, a degrading environment, harm to the wildlife and light trespass into yards and into bedrooms, deadly human health consequences, and the extinction of the the mystery of of starry nights.
Instead of staring up into a pristine dark night sky, looking for the star of Bethlehem high in the sky, artificial light displays blot out the sky and the stars. Sky glow created, which can be seen hundreds of miles away from the source.
How would the three wise men ever found the stable and manger holding the new born little baby Jesus with all of the light pollution and light trespass today?
Where would Christmas have come from? Maybe it is time to return to the days of yore.
Use light intelligently, smartly, responsibly, kindly and considerately.
Follow DarkSky International’s five lighting principles for responsible outdoor lighting.
Use a modicum of restraint especially with the holiday lights.
The planet and all her creatures thank you!
Eileen Kragie is the founder of Dark Sky Friends, an organization that advocates for responsible outdoor lighting at night.
Why Are So Many American Pedestrians Dying at Night?
Comments published in New York Times
Dark Sky Friends
Virginia
Glare from improperly designed and positioned lights, along with the bright LEDs from headlights, blinds drivers causing serious public safely hazards.It takes 10 to 15 minutes to regain your night vision after being blinded by light. With the exponential increase in the use of too high (lumens) of bright blue-white colored lights vs warmer color temperature (kelvins) lights, roads and streets are becoming much more dangerous. Businesses, homeowners and municipalites install light that trespasses and ones that do not illuminate the intended area.Dangerous public safety situations are created and oft times even after notifying the entity of the dangerous effect of the light, nothing is done to mitigate it.Most times it is only requires repositioning the fixture to point toward the ground or to add full shielding.With the lack of protection in the form of strict outdoor lighting ordinances and legislation, the problem of light pollution and light trespass only continues to worsen.Coupled with the other distractions affecting drivers this problem of pedestrian deaths will continue to grow.
Original article published in New York Times 11 December 2023
Why Are So Many American Pedestrians Dying at Night?
(Click on link for tables of statistics)
Sometime around 2009, American roads started to become deadlier for pedestrians, particularly at night. Fatalities have risen ever since, reversing the effects of decades of safety improvements. And it’s not clear why.
What’s even more perplexing: Nothing resembling this pattern has occurred in other comparably wealthy countries. In places like Canada and Australia, a much lower share of pedestrian fatalities occurs at night, and those fatalities — rarer in number — have generally been declining, not rising.
Pedestrian Death Rate at Night
In America, these trends present a puzzle that has stumped experts on vehicle design, driver behavior, road safety and how they interact: What changed, starting about 15 years ago, that would cause rising numbers of pedestrian deaths specifically in the U.S. — and overwhelmingly at night?
“This is something that, quite frankly, our profession missed,” Rebecca Sanders, the founder of Safe Streets Research and Consulting, said of the toll of nighttime deaths. “I think we missed that for a long time.”
In 2021, more than 7,300 pedestrians died in America — three in four of them during the hours between sunset and sunrise.
This trend exists on top of what is already a growing gap in roadway deaths between the U.S. and other countries. Speed limits on local roads are often higher in the U.S., laws and cultural prohibitions against dangerous driving can be weaker, and American infrastructure in many ways has been designed to enable speeding cars.
Those baseline conditions may mean, researchers suggest, that American roads — and the pedestrians walking along them — have been especially susceptible to potential new risks like smartphones and bigger vehicles.
But even that is only part of the picture.
“I don’t have any definitive answers for this,” said Jessica Cicchino, the vice president for research at the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety. Ms. Cicchino, like many observers, has puzzled over how rapidly nighttime deaths have risen. “What is it that’s happening specifically in the dark?”
The Danger of Darkness
For starters, it’s important to understand just how stark the threat of darkness is for pedestrians in the U.S. Federal data that tracks every roadway fatality makes clear that the problem is not just about the behaviors and routines that happen to occur around nighttime (leaving work, for example, or going to bars). It is darkness itself that matters.
This chart shows the deadliest time of day for pedestrians, averaging data from 2000 to 2021 over a whole calendar year:
Pedestrian Deaths by Time of Day
Source: New York Times analysis of federal road fatality data.
Another way of describing this picture: It shows the annual arc of the setting sun. Researchers have found related patterns looking at fatal collisions that occur in the weeks before and after clocks change for daylight saving time. When the 6 p.m. hour abruptly changes from light to dark, for example, even as traffic patterns generally remain the same, that hour becomes abruptly more deadly, too.
“It’s purely an effect of daylight or darkness — and it’s huge for pedestrians,” said Michael Flannagan, a retired professor at the University of Michigan.
In the dark, pedestrians are harder to see than other road users. They typically don’t wear reflective gear or lights, and their outerwear is often dark in color. American roads also weren’t particularly engineered with this risk in mind.
“We literally taught generations of engineers to design conditions for daylight and not to consider nighttime,” Dr. Sanders said.
The risk for other road users is higher during the day: The majority of deaths among vehicle occupants occur then. Until the last few years, that was true of cyclist fatalities, too. Even incidents of cars driving off the road don’t spike with nightfall in the same way that pedestrian fatalities do.
Darkness, it appears, especially threatens people on foot.
Or, rather, people on foot in America. In comparable countries, pedestrians are generally more likely to be fatally struck during the day.
New Risks
The most obvious potential risks that have changed in America since 2009 are found inside vehicles — in the drivers there fiddling with smartphones, in the dashboard displays that have grown ever more complex, in the growing weight and force of vehicles themselves.
Smartphones have become ubiquitous with remarkable speed, overlapping closely with the timeline of rising pedestrian deaths. Apple’s iPhone was introduced in 2007. Within a few years, one-third of American adults said they owned a smartphone. By 2021, according to the Pew Research Center, 85 percent did.
When it comes to other sources of driver impairment, “there’s no particular reason to believe that alcohol, speeding or fatigue necessarily have changed in any kind of big way,” said David Strayer, a psychologist who studies driving at the University of Utah. “What has changed is the amount of technology that we’re surrounding ourselves with.”
Smartphones — and the way they can distract both drivers and pedestrians — aren’t uniquely American. But there is one thing that is still distinctly so: the pervasiveness in the U.S. of automatic transmissions, which help free up a driver’s hand for other uses. Just 1 percent of all new passenger vehicles sold this year in the U.S. had manual transmissions, according to the online car-shopping resource Edmunds. In Europe, manual transmissions are declining in popularity as a share of new light vehicles sold. But they still make up about 70 to 75 percent of cars on the road, estimated Felipe Munoz, senior analyst at JATO Dynamics.
It’s perhaps not surprising then that Americans spend nearly three times as much time interacting with their phones while driving as drivers in Britain, according to smartphone data collected by Cambridge Mobile Telematics, which helps auto insurers, carmakers and local governments track and reduce dangerous driving. In the U.S., that distracted driving — detected when phones are tapped or in motion in vehicles traveling faster than 9 miles per hour — also typically peaks in the evening hours, according to the company’s data.
Time Spent Interacting With Phones While Driving
Source: Cambridge Mobile Telematics data covering about 920 million U.S. car trips from Jan. 2020-Oct. 2023.
Though this data doesn’t capture exactly what people are doing on their phones, evening is when people often coordinate social activities and manage after-hours work messages and tasks. America’s round-the-clock work culture may contribute to that trend.
“The adoption of smartphones for the past 15 years — where we are today, being addicted on social media and other apps — absolutely contributes to the increase in fatalities on our roads,” said Matt Fiorentino, Cambridge Mobile Telematics’ vice president for marketing.
Official data linking smartphones and crashes is hard to find, though, given that the police typically don’t ask people involved if they were using phones (and those people might not answer truthfully anyway).
Beyond just display screens, new vehicles have also changed to be wider, longer, taller and heavier. Not only do heavier vehicles hit pedestrians with more force, but they also often have worse brake times, meaning a driver who notices a pedestrian at the last second may strike that person at higher speeds. Studies have also indicated that vehicles with taller hoods are more likely to kill if they hit pedestrians; they strike people closer to the head or torso, instead of the legs.
While researchers have pointed toward vehicle size as a factor explaining America’s high overall rate of pedestrian fatalities, several said they were skeptical that it explains much of the increase since 2009. That’s because American cars were relatively large even before 2009, and the rate at which new cars replace existing ones is slow.
“In explaining the big run-up in pedestrian deaths, it’s not actually a huge portion,” said Justin Tyndall, an assistant professor at the University of Hawaii Economic Research Organization. His research estimates that the change in vehicle types since 2009 is responsible for less than 100 additional deaths per year. By comparison, around 3,300 more pedestrians died in 2021 than in 2009.
Similarly, ownership of smaller vehicles (like sedans, coupes and station wagons) is down since 2009. But total pedestrian deaths from these same cars are up more than 70 percent, suggesting the bulk of the problem cannot be attributed to increased car size alone.
The behavior of drivers inside vehicles — of any type — may also have changed over this time for a few additional reasons, researchers suggest. This timeline also overlaps with the rise of opioids and the legalization of recreational marijuana. But there is little research about how marijuana affects driving.
Periodic federal roadside surveys, last updated in 2013-14, have found declining alcohol use by drivers and a rising share testing positive for drugs. A more recent federal study, collecting data from trauma centers and medical examiners about seriously or fatally injured road users, found in the years leading up to the pandemic that half of the drivers studied tested positive for at least one active drug. During the pandemic, that share rose to 65 percent. The results, the authors warned, “could be indicative of a growing problem.”
Societal Change
None of the explanations so far easily accounts for the full rise of pedestrian fatalities in the U.S. But while less obvious than driver and vehicle behavior, changes that have happened outside the car and across American society may be just as important.
One theory is that Americans have been migrating toward the Sun Belt, including parts of the country that developed in the auto age, that have particularly poor pedestrian and transit infrastructure, and that have some of the highest pedestrian fatality rates. The rise in pedestrian deaths has been nationwide, with per-capita pedestrian fatality increases in 47 states since 2009. But many areas that have had poor pedestrian safety records going back decades — especially metro areas in Florida, Texas, and Arizona — have also seen the greatest recent population growth.
Yearly average calculated from 2019-2021.
Source: New York Times analysis of federal road fatality data.
The number of pedestrian fatalities in Florida has increased 75 percent since 2009, while the population has increased around 17 percent. Such state population changes alone don’t explain most of the rise in deaths, however. More relevant patterns may have to do with where, specifically, people have moved within those states.
Nationwide, the suburbanization of poverty in the 21st century has meant that more lower-income Americans who rely on shift work or public transit have moved to communities built around the deadliest kinds of roads: those with multiple lanes and higher speed limits but few crosswalks or sidewalks. The rise in pedestrian fatalities has been most pronounced on these arterials, which can combine highway speeds with the cross traffic of more local roads.
Research has found that pedestrian deaths over the last 20 years have declined in downtown areas and increased in the suburbs, often in places where lower-income residents live. Such suburban arterial roads are also where many communities have allowed multifamily and affordable housing construction that has been less welcome in neighborhoods with inherently safer streets.
In Portland, Ore., for example, immigrants and lower-income residents priced out of other parts of the city have moved in along some of the region’s most notoriously dangerous corridors, like 122nd Avenue, a five-lane arterial that runs through the city’s most racially and ethnically diverse neighborhoods.
“Now we have folks that are living, working, shopping, going to school directly on these roads that were essentially built as highways,” said Dana Dickman, the traffic safety section manager for the Portland Bureau of Transportation.
In more recent years, the rise of homelessness in many American cities since about 2016 has also put a growing vulnerable population on streets in conflict with speeding cars. In 2021, 70 percent of Portland’s pedestrian fatalities were among the homeless. Last year, about a third were, similar to recent data in Los Angeles. Such data is relatively limited and new, but other cities including Colorado Springs and San Jose, Calif., have also noted a rise in pedestrian fatalities among the homeless.
The homeless population may have little choice but to be out at night, and near dangerous roads.
“Where they’re actually living unhoused — next to freeways, next to undercrossings — those are typically places that are busy streets,” said Tim Weisberg, a deputy director for the California Office of Traffic Safety.
Nationwide, the overwhelming majority of the rise in pedestrian deaths since 2009 has come among working-age Americans, reinforcing the idea that this shift may also have to do with where those people are living and spending time.
Change in Pedestrian Death Rate by Age
Source: New York Times analysis of federal road fatality data.
People 17 and under are the one group bucking the overall trend, and deaths of children walking are at a record low. Not only are children less likely to be walking at night when the majority of pedestrian deaths occur, but studies have also estimated that the percentage of children who walk or bike to school has declined precipitously over the last 50 years.
Individually, any of these theories seems unsatisfying. But put together, it’s clear that there’s been a particularly American mix of technological and social changes over the past decade and a half. And they have all come on top of a road system and an ingrained culture that prioritizes speed over safety. Whatever has happened over this time has reversed years of progress on daytime pedestrian fatalities, too, leading to a modest increase in deaths. Nighttime, however, has the potential to amplify so many of these new risks.
A transportation system that’s safer by design — as in many European countries — might better absorb any one of these dangers. Distracted drivers are safer at lower speeds. People out at night are safer with well-lit crosswalks.
Even “monster trucks are safe on safer roads,” said Nicholas Ferenchak, a professor at the University of New Mexico and director of the Center for Pedestrian and Bicyclist Safety.
Now imagine distracted drivers in monster trucks on high-speed roads in the dark.
Methodology
Data on U.S. fatalities comes from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration’s Fatality Analysis Reporting System, which records all roadway fatalities and variables about each incident, including the time, location, road and vehicle type involved and age of the deceased. The Times analysis identified nighttime deaths by comparing the recorded location of each pedestrian fatality with the time of sunset or sunrise at that location on that date. Unless noted, cyclists and other individuals not explicitly labeled pedestrians in the data were not included in our analysis.
International pedestrian fatality data comes from the Australian Road Deaths Database, Britain’s Department for Transport, Canada’s National Collision Database and France’s Observatoire National Interministériel de la Sécurité Routière.
The group of “smaller vehicles” refers to those categorized as “passenger vehicles” by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and Federal Highway Administration. This includes sedans, coupes, convertibles, hatchbacks and station wagons — but not trucks, minivans or S.U.V.s. Registration data was used to track declining vehicle ownership among this group.
Artificial Light at Night Leads to Plant, Pollinator Decline
Illuminating Solutions To Reduce Sky Glow
by Christina Tyler Wenks, Fairfax Master Gardener
Light pollution impacts the health of wildlife, pollinators, plants and humans, but residents can take simple steps to reduce a problem that is increasing as much as 10 percent each year.
Illuminating Solutions To Reduce Sky Glow
Originally published in Fairfax County Master Gardeners Fairfax Gardening
by Christina Tyler Wenks, Fairfax Master Gardener
Light pollution impacts the health of wildlife, pollinators, plants and humans, but residents can take simple steps to reduce a problem that is increasing as much as 10 percent each year.
International Dark Sky Association suggestions to reducing night light
Illuminated landscapes are a distinguishing characteristic of industrialization and cover much of the Earth’s surface, but life evolved to need hours of darkness. Exposure to artificial light at night can disrupt organisms’ physiological processes with implications for health and conservation and contributes to the decline of some plant and pollinator populations.
Lights allow longer work, play, productivity and make people feel safer, but the problems caused by excessive lighting are far reaching — even into space. Pockets of purely natural light are becoming the exception, not the rule. Just as cooperative extension agents and certified master gardeners suggest the “right plant in the right place,” one solution to light pollution and subsequent sky glow could be as simple as right light at the right time pointed in the right direction.
Earth is transitioning from nighttime to lighttime
More than one-third of the world’s population, which includes 80 percent of the United States population, cannot see the Milky Way or constellations due to artificial light at night, also known as ALAN, which is caused by house and street lights, vehicles and commercial lighting. Disappearing night sky has health consequences to nocturnal wildlife, pollinators and plants as well as human mental health.
LED-lighting provides less expensive and brighter, intense-white lighting, which stimulates the popularity growth of upward aesthetic landscaping lighting with light directed at foliage and structures. Extra light traveling up into the night sky contributes to sky glow, which appears brighter under reflective nighttime clouds.
“Artificial light changes the circadian rhythm of beings and is a type of climate change that is controllable and reversible,” says Eileen Kragie of Dark Sky Friends, a nonprofit based in Fairfax County, Virginia, dedicated to educating about the impact of light pollution and light trespass and how to reverse it.
A newly opened exhibit at the Smithsonian’s Natural History Museum called “Lights Out: Recovering our Night Sky” illuminates the perils of sky glow as well as solutions to reverse ALAN without diminishing visibility or safety. The timing of the exhibit at the Natural History Museum on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., coincides with emerging and growing research about exposure to artificial light at night disrupting organisms’ physiological processes with implications for health and conservation.
Plants, pollinators, predators and prey
Plants and trees depend on light wavelength or color, light intensity or brightness, and hours of light duration to govern photosynthesis that requires visible blues and reds to stimulate sugar production. A plant’s photoperiodism, caused by red and infrared light, controls vegetative and reproductive activities, which is why artificial light at night can cause plants to leaf out instead of flower or fruit.
Photinus pyralis firefly
ALAN impacts the food web in unprecedented and unpredictable ways and is blamed as a cause for the population decline of fireflies that are attracted to any form of light. Fireflies or lightning bugs live underground for years before emerging above ground and using bioluminescence to attract a mate. Most active at dusk and just after dark, males in the treetops fly down to the females that flash, flicker or glow just above the ground. ALAN confuses lightning bugs.
Increasing artificial light around plants that open solely at night or are pollinated by nocturnal pollinators like bugs, birds and bats, decreases or prohibits plants from flowering and reproducing, which impacts plant reproduction and pollinating species, too.
Nighttime croaking is part of the breeding ritual of frogs and toads. Artificial light disrupts nocturnal activity, interfering with reproduction and reducing populations.
Caterpillars often use the guise of night to feed and avoid predation. Insects at all life stages and aquatic organisms caught in artificial light become late-night snacks, reducing populations and impacting long-term sustainability.
Research finds predatory arthropods such as spiders are disproportionately represented in illuminated habitats, and owls are adapting to artificial lighting and nesting nearer to night lights to extend successful foraging time, but the absence of dark is consequentially foul for fowl health, too.
Window light, barred owl eats bugs
During an April 2023 Smithsonian Institution webinar called “Lights Out: the Effects of Light Pollution on Bird Health,” biologist Biologist Valentina Alaasam discussed her ongoing research examining the effects of light pollution on the health of birds and what that research demonstrates about animals adapting to an environment where more light at night is the new normal. Alaasam’s research showed that birds are less likely to nest in trees above yard lights and birds try to nest in darker spaces. In urban and suburban areas, birds have fewer dark choices and nest where they must.
Her research shows that birds subjected to light pollution all night for weeks had enlarged hearts, an effect she said is comparable to heart disease in humans, and young birds are developmentally impacted, too. But, she said her team’s research shows that negative health symptoms caused by all-night light can be reversed within a few weeks when birds return to nesting in all-night darkness. The research parallels studies about human sleep patterns and behaviors and further research is underway.
Research shows that the type of light impacts the amount of nighttime predation and health consequences. Energy-efficient LEDs can create a much brighter, sharper, white light compared to the low-pressure yellow-orange glow of older streetlights, but newer LEDs offer adaptive options such as adjusting color and intensity that can add additional efficiency and appliance longevity and, if used optimally, can be part of respectful night light that coincides with energy cost savings.
Regaining the night requires community involvement
To regain dark skies, respect Native American cultures, to support astro-tourism, and the health of all beings, Tucson, Arizona, leaders made a city-wide lighting retrofit that can be applied anywhere in the world. Down-facing, directional, energy-efficient LED-based lighting saves the city thousands in electricity. Tucson optimized lighting-color temperatures to warm hues specific for different periods of night, operating LED lights at 60 to 90 percent intensity, resulting in energy cost savings.
The City of Alexandria, Virginia, is committed to deliberate, directional lighting endeavors, too, and in a 2023 Dark Sky Proclamation detailed the city’s intent to protect neighborhoods adjacent to stadium lighting from light trespass, too.
Virginia leads the nation in proclamations supporting dark skies with state and municipal support from Arlington, Falls Church, Vienna, Leesburg, Lexington, Ashland and more.
Fix light pollution with four Rs
National Public Radio reports that light pollution is increasing 10 percent every year, but researchers assert that humans can reverse the trend.
Simple, immediate solutions include:
Reduce light at night by using the least amount only where and when needed and remove redundant lighting. Lights should be turned off or dimmed during off-peak hours to avoid continuous lighting of trees, which has the greatest potential for upsetting normal growth patterns. While shade trees can mitigate light pollution, trees and wildlife in trees are affected by ALAN. Where night lighting already exists, select plantings with low sensitivity to light. Use dimmers, timers and motion sensors.
Replace blue and white light with warmer lights that may have less light intensity. Use timers and sensors that turn on/off lights.
Re-direct amounts of light by using lamp covers or directional lighting fixtures facing the ground to reduce light spilling up into the night sky to prevent light pollution avoiding blinding glare. Researchers and Dark Sky Association members recommend avoiding all upward lighting and shining light over horizontal distances.
Research is ongoing and needed.
Alaasam said that reducing the amount of light from urban commercial and suburban home windows by 50 percent can reduce the number of bird collisions into buildings because of disorienting light at night.
Technology aids adapting lighting, color and intensities where and when needed. The right color and intensity of light at the right time pointed in the right direction creates the right light at night.
Resources
• Lights Out: the Effects of Light Pollution on Bird Health, Smithsonian Institution, webinar, April 12,
2023
• Lights Out: Recovering Our Night Sky Exhibition, Smithsonian Natural History Museum
• Planet Positive Worldwide Lights Out Program, Smithsonian Magazine
• All Things Considered, Light pollution frustrates astronomers looking for discoveries, National Public
Radio (NPR),
• A review of the effects of artificial light at night in urban areas on the ecosystem level and the
remedial measures, Frontiers
• Light pollution harms plants in the environment, Florida Atlantic University
• Light Pollution Effects on Wildlife and Ecosystems, International Dark Sky Association
Bat Festival 2023 at Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts
Originally published in HappeningNext
Bat Festival: "Protecting Our Nocturnal Neighbors" ~ Join us for lots of bat fun!
About this Event
Sun Oct 29 2023 at 03:00 pm to 06:00 pm
Host: Dark Sky Friends
Join us for a captivating afternoon at Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts as we celebrate and learn about these incredible creatures of the night at the "Bat Festival: Protecting Our Nocturnal Neighbors." This educational event is designed to shed light on the importance of bats in our ecosystem, raise awareness about the threats they face, and empower attendees to take action to protect them.
Image credits: Leslie Sturges -3 bats, eileen Kragie -sunset, Bat images by Freepik
Highlights of the Festival:
1. Bat Education and Conservation Talks:
Renowned bat experts will share their knowledge about the diverse world of bats, their ecological significance, and the threats they encounter, including light pollution.
Including Leslie Sturges, President Bat Conservation and Rescue Virginia and Alonso Abugattas, "The Capital Naturalist"
Learn how you can make a difference in bat conservation efforts.
2. Light Pollution Awareness:
Discover the detrimental effects of light pollution on bats and other nocturnal wildlife.
Learn how simple changes in lighting practices can make a big difference.
3. Bat-Themed Activities and Educational Tables
Engage in fun, interactive activities for all ages, costumes optional and costume contest
4. Food and Refreshments:
Bring your own blanket, chair, picnic and favorite beverage. Food/beverages will not be available for purchase at event.
5. Conservation Partners:
Connect with local and national organizations dedicated to bat conservation and other conservation efforts.
Bring your friends and family for an afternoon of fun, education, and a deeper appreciation for the vital role bats play in our ecosystem. Let's work together to reduce light pollution and ensure a brighter future for these remarkable nocturnal neighbors.
Reserve your spot today and be a part of this unique and enlightening experience!
Registration is FREE
Event Partners:
Dark Sky Friends
DarkSky International
DarkSky NOVA
National Park Service
Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts
Friends of Wolf Trap
Fairfax County Park Authority
Bat Conservation & Rescue of Virginia
The Capital Naturalist
Audubon Society Northern Virginia
George Mason Observatory
Analemma Society
NASA JPL Solar System Ambassador
and more....
</ul>
Safety Note: Your safety is our top priority. Please follow all event guidelines. For your preparation and safety for this outdoor festival, please bring a flashlight and cover with red film. Wear shoes appropriate for uneven ground and dress in layers.
In the case of heavy rain, inclement weather or government shut-down, this event will be cancelled.
Participants assume full liablity for attending and cannot hold sponsors, hosts, volunteers liable for any injury or mishap. By registrering, the participant HEREBY AGREES TO WAIVE, RELEASE, DISCHARGE INDEMNIFY AND HOLD HARMLESS listed FROM ANY AND ALL CLAIMS FOR DAMAGES FOR DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY OR PROPERTY DAMAGE WHICH MAY HEREAFTER ACCRUE AS A RESULT OF ANY PARTICIPATION.
I grant full permission to use and reproduce my images or likeness by any audio and/or visual recording technique (including electronic/digital), for any legitimate purpose, including commercial marketing purposes, relating to the Event or to promote awareness and fundraising
Advertisement
Where is it happening?
Wolf Trap National Park for the Performing Arts, 1551 Trap Road, Vienna, United States
The dark legacy of artificial light
This article was originally published in Letters to the Editor The Washington Post Opinion Readers critique The Post: Hold climate change culprits accountable September 15, 2023 at 7:00 a.m. EDT
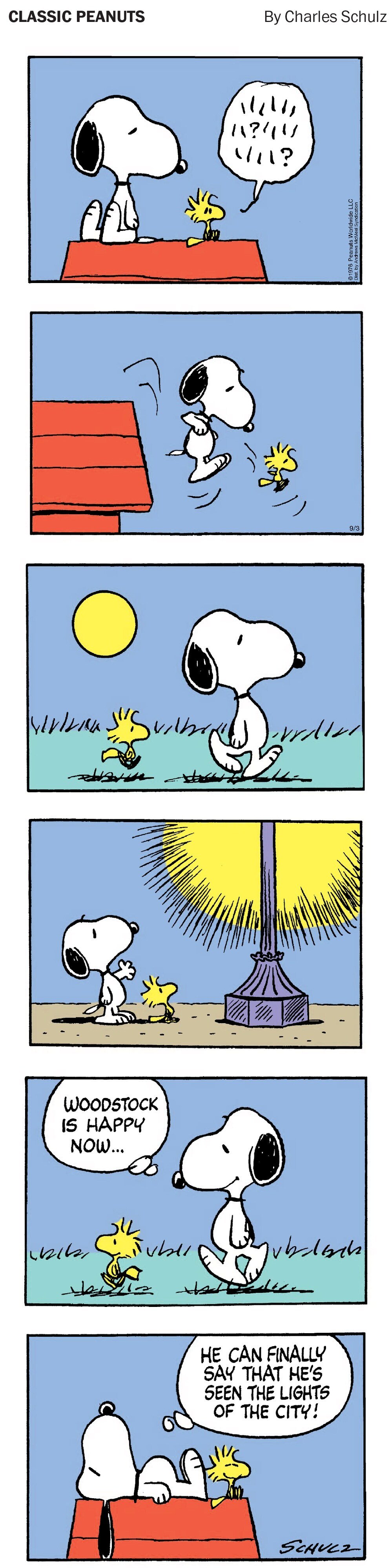
The Sept. 3 “Classic Peanuts” comic strip was too depressing for words.
Woodstock’s reaction most likely would be one of horror these days at the explosion of irresponsible light at night, not only in the cities but also across the globe. The unshielded light depicted in the fourth frame causes glare, light trespass and light pollution.
The fall migration of the birds is beginning. Artificial light at night is the cause of death of hundreds of millions of birds each year.
One hardly thinks Woodstock would be happy seeing the pavement below buildings littered with the bodies of his friends. The “Lights Out: Recovering Our Night Sky” exhibit at the National Museum of Natural History shows what the unabated exponential growth of our artificial lights is doing.
Eileen Kragie, Vienna
The writer is the founder of Dark Sky Friends.
Fairfax supervisors OK lighting restrictions around observatory
More than 500 homes in Great Falls will be impacted by decision
Originally published in gazetteleader
Brian Trompeter Nov 27, 2023 10:11 AM
Photo Credit © Adobe Stock photo
New outdoor-lighting rules approved unanimously by the Fairfax County Board of Supervisors on Nov. 21 aim to ensure night skies above Turner Farm Park Observatory in Great Falls will not be subject to worsening light pollution – at least from the surrounding neighborhood.
“Although Fairfax is in an overall area of light pollution, due to the scientific properties of light, lighting near the observatory has a greater impact on the ability to view the night sky from that location,” said Deputy Zoning Administrator Carmen Bishop, who led the staff presentation at the meeting.
The new outdoor-lighting rules are designed not only to reduce light pollution, but also improve safety and security, she said. A total of 525 residential properties will be impacted.
Following their approval in February 2020 of a zoning-ordinance amendment that updated county outdoor-lighting standards, supervisors directed county staff to consider further zoning rules to protect dark skies around astronomical facilities.
(See new rules below.)
State law allows localities to regulate outdoor lighting within a half-mile radius of astronomical observatories, meteorological laboratories and planetariums.
The new rules, which took effect the following day, only regulate Turner Farm’s. The observatory at George Mason University’s observatory at its Fairfax campus is not subject to the county’s regulations, because it is on state-government property.
The Turner Farm property, which Fairfax County obtained in 1998, formerly was used by the Defense Mapping Agency and as a Nike missile-control site. Besides the observatory, the park also has equestrian facilities.
The observatory opened in 2016 and since January 2018 has served more than 16,500 people through viewing sessions and educational programs, officials said.
The Analemma Society, whose volunteers staff Turner Farm Observatory Park, is seeking to have the International Dark Sky Association designate the site as an Urban Night Sky Place.
“The observatory is an important and unique STEM educational resource that may serve to inspire students in their pursuit of further education and training and eventually join the STEM workforce,” said Jennifer Falcone, who chairs the Great Falls Citizens Association’s Land Use and Zoning Committee.
“The evolution of lighting technology and the introduction and popularity of bright LED lighting, GFCA believes this measure is especially appropriate,” added Falcone, who lives within the zone affected by the new lighting standards. “This amendment is not onerous . . . Security is not compromised by dark-sky-compliant lighting.”
Artificial light has been doubling every 10 years and causing sky glow, hence threatening the Turner Farm observatory, said Christina Tyler Wenks, an Analemma Society board member who volunteers at the site.
“Without action to preserve the night, our observatory has 10, maybe 15, years left,” Wenks said in video testimony.
Modern LED lights are significantly brighter than old-fashioned incandescent bulbs, said Eileen Kragie, president of Dark Sky Friends. Light crosses property boundaries and into people’s bedrooms, as well as public parks and common sky, she said.
“I don’t have the right to trespass onto your property,” Kragie said. “Why do my lights? Nothing onerous is being asked of anyone – simply to have kind, considerate and responsible lighting.”
Support for the amendment has not been unanimous in the community, said Supervisor John Foust (D-Dranesville). An Oct. 18 Planning Commission public hearing drew several neighbors of the observatory who protested the proposed regulations, citing property rights and security concerns.
County staff modified the proposed amendment following public feedback and the final result is a “very reasonable approach to the challenge that we have,” Foust said. “I just think this is a wonderful way to start the process of trying to preserve a sky that we can observe through the telescopes. Really [the observatory is] unique. It’s not like anything else we have in this county.”
Supervisor Daniel Storck (D-Mount Vernon) said he hoped the new rules would be the start of a mostly voluntary effort to reduce light pollution in the county.
Supervisor Penelope Gross (D-Mason) thanked those who testified at the meeting for their educational remarks.
“We don’t necessarily need all of that light,” she said. “I really do hope that Turner Farm Park will be able to serve future generations and that we can keep it relatively dark there.”
• • •
Under the new rules:
> Legally existing lights may remain until replaced by their owners, who then will have to buy lights that meet the new standards.
> Motion-activated lights on single-family residential lots need not meet the full cut-off or setback/shielding requirements if they are 1,500 lumens or less (equal to about one 100-watt incandescent bulb), versus the standard of 4,000 lumens or less for the rest of the county. In addition, those lights must continue to comply with existing standards requiring them to turn off within five minutes and be directed within the property.
> All outdoor lights must have full cut-off features and comply with setback and shielding regulations, except ones putting out 20 lumens or less and lights near doors and garages generating no more than 1,500 lumens per fixture.
> Uplights or spotlights highlighting flags, landscaping or architectural features now are limited to 300 lumens apiece, with no limit on the number of fixtures.
> Outdoor lights must have a color temperature no higher than 3,000 degrees Kelvin, the same as elsewhere in the county.
> There may be any number of lights, and of any brightness, provided they have full cut-off shielding.
Fairfax County updates zoning rules to allow brighter outdoor signs
An office building in Tysons displays a U.S. flag on an electronic sign (staff photo by Angela Woolsey FXXnow)
Originally published in FXXnow November 27, 2023 at 3:30pm
Electronic signs on display at eligible businesses, schools and other establishments can now shine brighter at night.
In planned, commercial and industrial zoning districts within Fairfax County, electronic display signs can now reach brightness levels of up to 300 nits at night, compared to 100 nits previously.
The Board of Supervisors unanimously approved the change to the county zoning ordinance after a public hearing at its Nov. 21 meeting.
“Nits” indicate an object’s brightness. Common cellphones, televisions and computer monitors have nit levels between 250 and 600, according to a county staff report. Under existing county rules, a lot has a designated amount of “freestanding sign area” and may have one electronic display sign that uses up to 50% of that area.
“During outreach on this amendment, we did receive feedback from industry that modern screens are getting brighter, including the widespread use of LED technology,” said Casey Judge with the county’s Department of Planning and Development.
Feedback and research led to county staff’s recommendation to increase the maximum brightness, Judge said.
In residential districts, the maximum nit level will remain 100 nits at night. The 100-nit limit will also apply to any electronic display signs visible to a single-family dwelling within 150 feet of the property with the sign.
Staff had recommended increasing the maximum nit level to 500 nits in planned, commercial and industrial areas in an Oct. 3 report. However, the Fairfax County Planning Commission recommended the ultimately approved 300-nit maximum and the 100-nit maximum for signs located near single-family homes, Judge said.
“I’m not sure 150 feet is the right number, but I think this is one of those things, over time, we’ll probably be getting feedback if it’s too short,” Hunter Mill District Supervisor Walter Alcorn said.
Three community members spoke during the public hearing. Kenny Peskin, a McLean resident who identified himself as an employee of the International Sign Association, said he was “generally in support of the motion,” in particular the version in the staff report with the higher nit limit.
Eileen Kragie, founder of an organization called Dark Sky Friends that advocates against light pollution, spoke against artificial light at night, but called the work “a credible first cut for the electronic signage ordinance.”
Jennifer Falcone called in on behalf of the Great Falls Citizens Association, reporting that the board of the association supported the motions adopted by the planning commission.
Changes to the zoning rules for outdoor signs have been in the works for over a year. Staff presented an initial proposal in May that underwent two public hearings with the planning commission.
Other approved changes include combining three sign application processes and permitting illuminated window signs of up to 4 square feet in non-residential locations.
County staff will provide a report on the implementation of the new guidelines within 18 months.
(For full public hearing Special lighting Zone and electronic signage Fairfax county Board of Supervisors meeting 21 Nov 2023
go to 4:34:22 for testimony by Kragie for signage amendment portion of public hearing)
County board of supervisors approves zoning changes to curb light pollution in Great Falls, Virginia - The Observatory at Turner Farm Park
The roll-top observatory at Turner Farm Park (courtesy Fairfax County Park Authority)
Originally publishes in FXXnow - Fairfax County Now County board approves zoning changes to curb light pollution in Great Falls
Written by Fatimah Waseem 28 Nov 2023
(Updated at 4:55 p.m.) After more than two years of development, a new set of regulations will officially preserve dark skies around Turner Park Farm Observatory in Great Falls.
At a meeting on Nov. 21, the Fairfax County Board of Supervisors unanimously approved zoning changes that aim to reduce light pollution and preserve dark skies within a half-mile of the observatory.
The proposal was significantly pared down after several community meetings and town halls. The changes will only apply to future lights on properties located within a half-mile of the observatory.
Dranesville District Supervisor John Foust said he was satisfied with the proposal, which he called a “very reasonable approach” to the challenge facing the community.
“It’s not unanimous in the community, but I will say that the opposition is much less almost justified than it was when this thing started,” Foust said.
Under the zoning ordinance amendment, motion-activated outdoor lights must be 1,500 lumens or less — a drop from the current limit of 4,000 lumens or less.
Additionally, all lights need to be fully cut off — meaning the bulb can’t be exposed — which is currently not required. Still, an exception to the cut-off and shielding requirements will remain for lights at a door or a garage of up to 1,500 lumens per fixture.
The regulations would also set limits on the number of up-lights or spotlights allowed. Currently, any number are allowed as long as they’re fully cut off or shielded to confine light. The changes would limit each fixture to 300 lumens.
Unlike at previous public hearings, divisive testimony was limited. Several testifiers spoke in favor of the changes to the zoning ordinance.
Jennifer Falcone, a representative for the Great Falls Citizens Association, said the proposal is integral to protecting a “treasured community resource.”
“I live within this area,” Falcone said. “Given the evolution of lighting technology and the introduction and popularity of LED lighting, GFCA believes this measure is especially appropriate.”
Eileen Kragie, president of Dark Sky Friends, a nonprofit organization that aims to preserve dark skies, emphasized that the changes are sorely needed.
“Light pollution is growing at twice the rate of the population,” Kragie said. “In 20 years, stars won’t be visible.”
Mount Vernon District Supervisor Daniel Storck said the proposal’s approval could pave the way for future changes.
“This is in my mind…the start of a process that is mostly voluntary,” Storck said. (The spelling of Supervisor Storck’s name has been corrected.)
The amendment’s passage came on the same day that the Board of Supervisors approved zoning changes that will permit brighter electronic signs in more urbanized and commercial districts.
Fairfax County Board of Supervisors Great Falls light Reston Turner Farm Parkzoning
Fairfax County BOS Unanimously Passes Special Lighting Zone around the Observatory at Turner Farm Park 21 November 2023 meeting
The Observatory at Turner Farm Park, Great Falls Virgnia
Photo credit: Eileen Kragie
A Public Hearing on a Proposed Zoning Ordinance Amendment Re: Outdoor Lighting Around Turner Farm Park Observatory (Dranesville District) was held by the Fairfax County Board of Supervisors 21 November 2023 meeting.
The amendment for the special lighting zone passed unanimously which serves to protect the night skies over and around this observatory and the Great Falls community for all future generations. Pristine night skies along with a healthy environment for all are quickly being lost to runaway light pollution and light trespass.
This step to protect and to preserve the night skies and nocturnal environment in Fairfax County is a first step in reversing and in beginning to reclaim our birthright to the night skies above us and to a healthy nighttime environment.
Dark Sky Friends founder Eileen Kragie testimony at board hearing
go to 4:03:20 for remarks from Kragie on the Observatory at Turner Farm Park special lighting zone
Full hearing on Special lighting Zone and electronic signage
go to 4:34:22 for additional testimony by Kragie for signage amendment portion of public hearings